Heat recovery in livestock buildings: smart energy savings
What is heat recovery?
Heat recovery is a technology where the heat from exhausted stall air is reused via the air scrubber to preheat incoming air or as an energy source for a heat pump. This reduces the need for additional energy from external sources such as gas or a heat pump power. Heat that would otherwise be lost is effectively utilised, resulting in direct savings on energy costs.
Especially in environments with high ventilation requirements, such as livestock farms or industrial buildings, this is a cost-effective solution. By extracting air flows in a controlled way and recovering them via heat exchangers, a stable and healthy indoor climate is achieved, at lower costs.
How does heat recovery work?
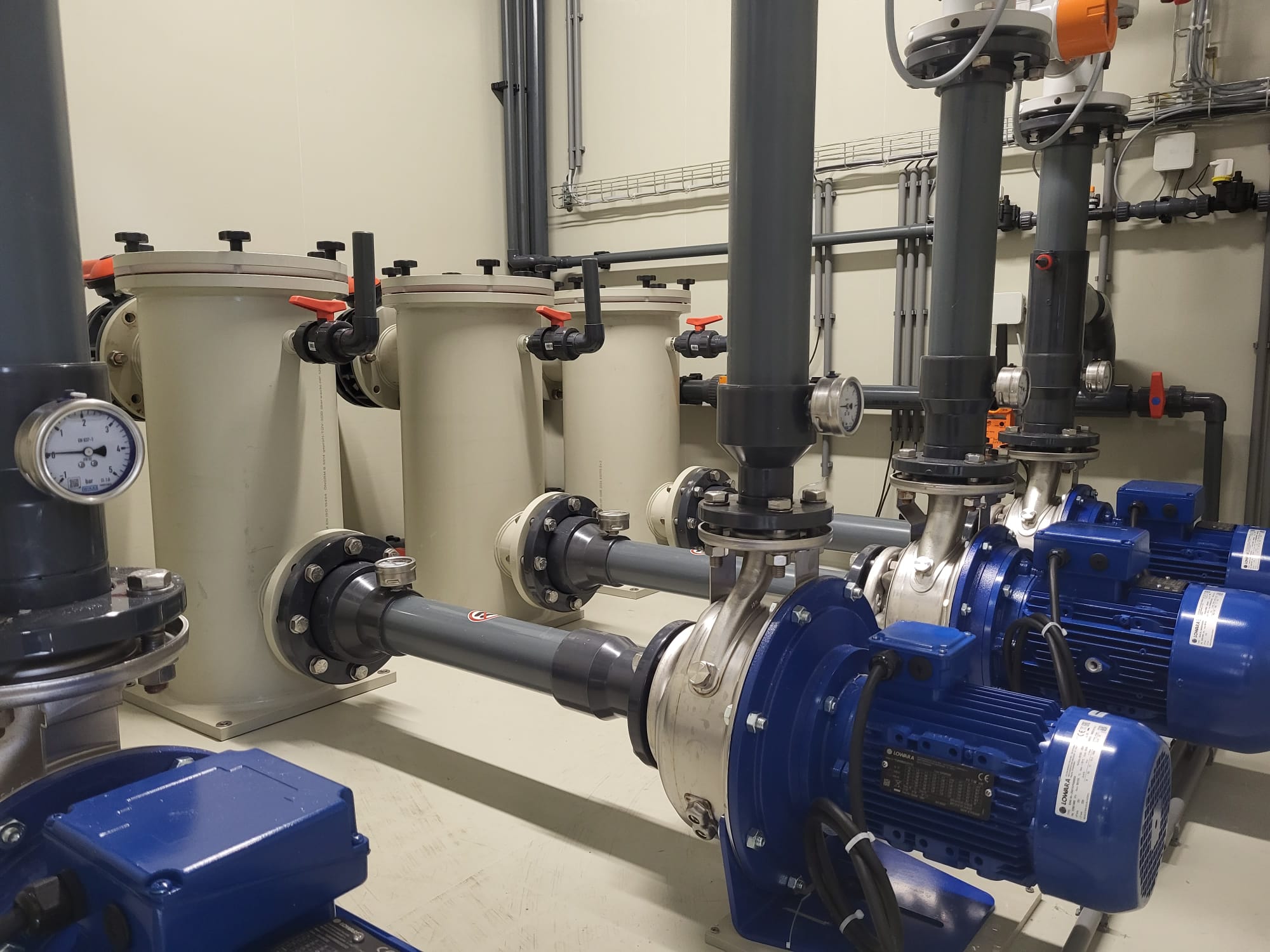
The heat recovery system uses the air scrubber as a heat exchanger. Polluted, warm farm air is discharged through a separate duct and heats the process water. The heated process water is sent over a plate exchanger via a pump. Here, the heat is transferred to the clean-water side of the system. This hot water is then sent directly to a heat exchanger in the air intake of the barn. This heats up the incoming air by up to 15 degrees.
In barns with central and mechanical ventilation, this process is automatic. Sensors monitor air quality and temperature, and control ventilation. In some installations, the recovered heat is further heated by a heat pump for space heating use.
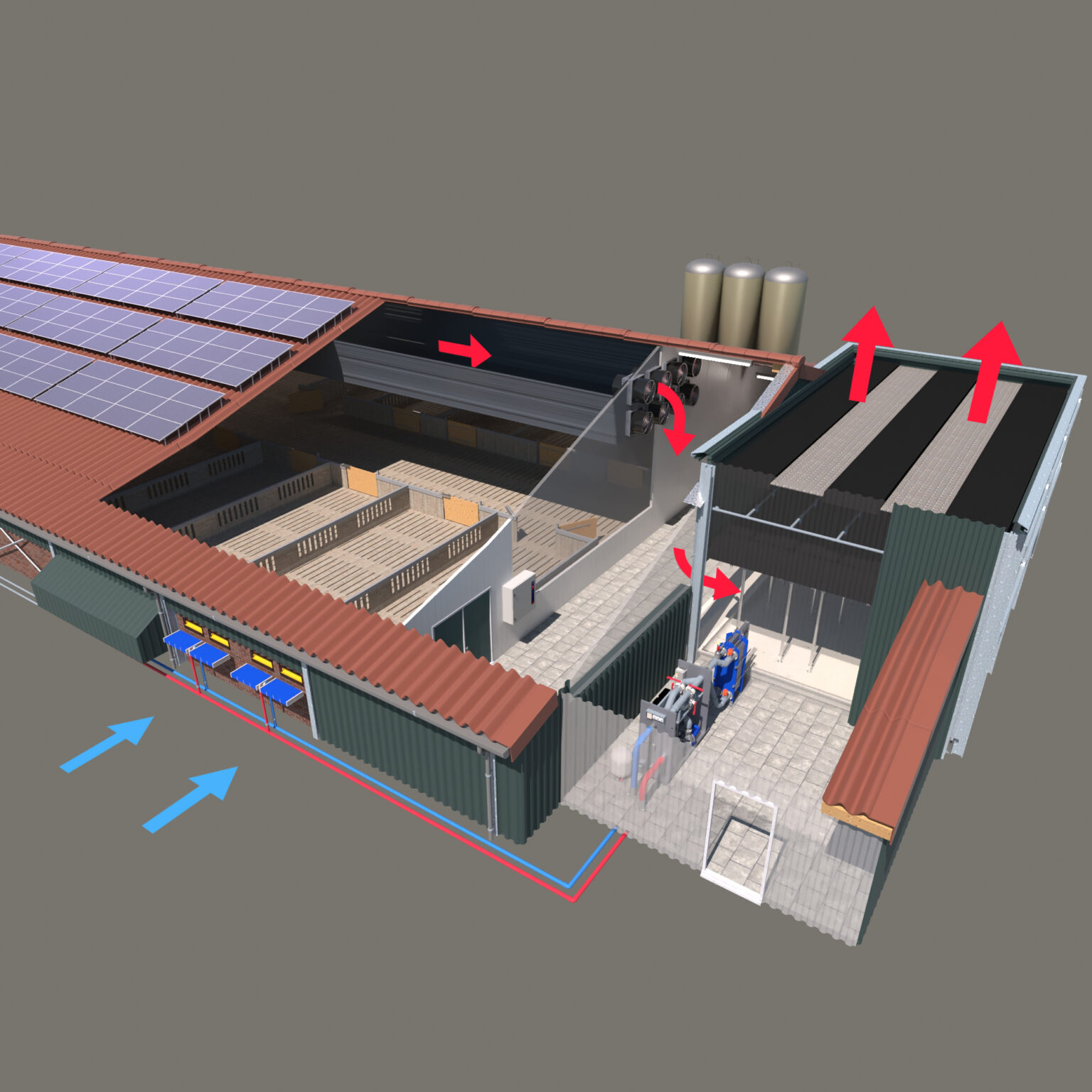
Key benefits
- Lower energy costs: The incoming air is already preheated, reducing the energy consumption of the heating system.
- Higher system efficiency: The efficiency of the overall climate system increases, especially when combined with mechanical ventilation or a heat pump.
- More constant barn climate: Less temperature fluctuations and fewer draughts improve animal health and increase productivity.
- Improved air quality: Pre-heated air ensures that the ventilation level does not have to be regulated too far back. This ensures a drier barn air without moisture problems and excessive levels of CO2 and ammonia in the barn.
- Less CO₂ emissions: Reusing waste heat reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
- Eligibility for subsidies: Various tax schemes make the investment more attractive and speed up the payback time.
- Broadly applicable: Not only for livestock farming, but also for greenhouse horticulture, industry, sports facilities and utility buildings.
- Greater operational reliability: Less dependence on energy prices makes your business more resilient and future-proof.

Practical application: heat recovery in livestock farming
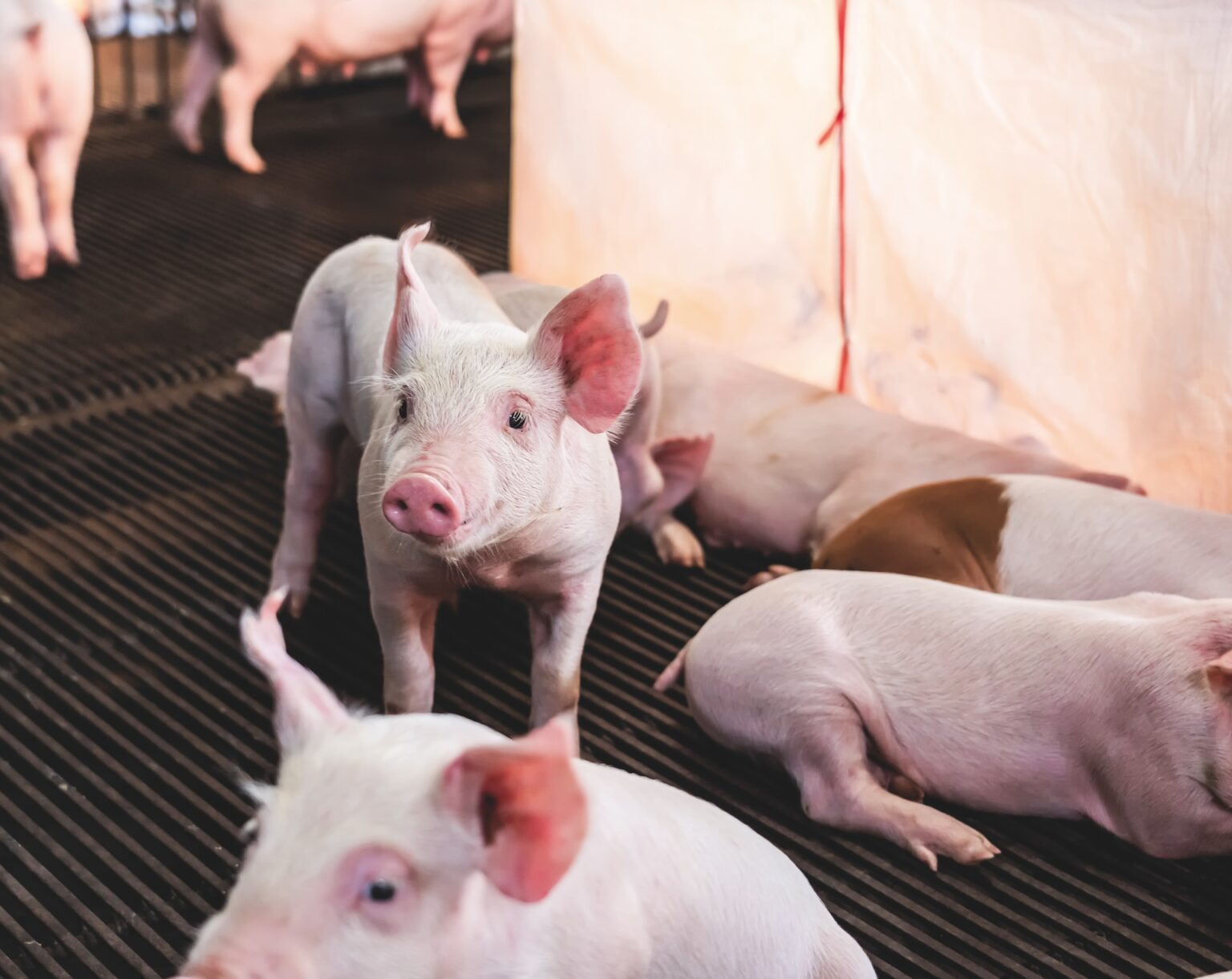
In modern livestock housing, a stable indoor climate is essential. Young animals such as piglets or chicks are sensitive to draughts and cold. By cleverly using warm outgoing air to heat incoming air or floor heating, energy costs can be reduced without compromising on animal welfare.
In systems where heat recovery is combined with air scrubbers, the warm air is used to heat water. This enables efficient and sustainable ventilation even in cold periods.

